Physics Calculators The wellknown American author, Bill Bryson, once said "Physics is really nothing more than a search for ultimate simplicity, but so far all we have is a kind of elegant messiness" Physics is indeed the most fundamental of the sciences that tries to describe the whole nature with thousands of mathematical formulasSolution for A 900 kg mass is moving to the right with a velocity of 140 m/s A 1 kg mass is moving to the left with a velocity of 500 m/s Assuming thatThe ball is acted upon by a constant gravitational force, mg The work done during its total trip, then, is simply mgh By the WorkEnergy theorem, this causes a change in kinetic energy Since the ball initially has no velocity, we can find the final velocity by the equation Solving for v, I understand
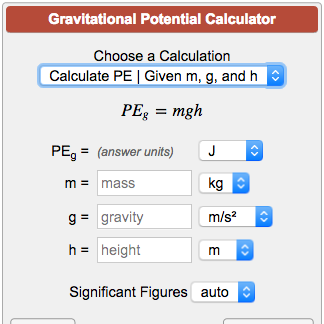
Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator
W=mgh solve for m
W=mgh solve for m-Know More × Contact Us Contact Need assistance?And mass = m and vertical height= H and gravitational force= g W= mgh Examples For Work Done in Raising a Box Solution Work done due to mg depends on height only For More Physics formulas vist main page and do solve exercise of NCERT from Entrancei NCERT solutions for class 11 Physics and NCERT solutions for class 12 Physics




Chapter 6 Work And Energy Pdf Free Download
F = m !a The unit of force is the unit of mass times the unit of acceleration LetÕs check that work has the same dimensions as energy Work equals force times distance So a unit of work is a Newtonmeter 1 Newtonmeter = 1 (kg m s2) m = 1 kg m 2/s2=1 JouleTo put it simply, gravity does do work on every object that is falling due to gravity The work done by gravity on a falling object depends only on the total change in height, given by the formula W=mgh If an object is not falling (its height doesn't change), gravity does not do any work on it The proof for this is extremely simpleUse the xcomponent from part (c) and substitute the given values Part (e) Using these same values, what is the ycomponent of the acceleration, in meters per second squared?
Contact us on below numbers For Study plan details /Part (d) If xB = 035 m, yB = 031 m, xC = 021 m, yC = 17 m, and the time interval Δt = 06 s, what is the xcomponent of this acceleration, in meters per second squared?I think the better question is "What does mgh stand for symbolically in physics and what is its significance?" Because this is my interpretation, I will answer the question in this fashion mgh is asking for the product of three variables "m" is
Hence M = Torr × g mol−1 = 9059 g mol−1 Torr In experiment · Newton's second law states F = m*a, in which a is the acceleration In the case of gravitation, a = g = 9,1 m/s² Work = W = F*s In case of gravitation, F = m*g, and s could be represented by h (height) The work done equals the change of potential energy So potential energy U = W = mghSolve for the indicated letter Each equation is from the indicated technical area of application W = mgh 2 mgh 1 , for m (work done on object)




Let Us Consider An Equation 1 2 M V2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of




Get Answer A Ball Is Dropped From A Height Of La M What Is Its Velocity When Transtutors
· Thus, work done by the force of gravity is W= Force × displacement =Weight × height = mg × h Thus, work done by force of gravity, W =mgh Similarly, if the body is thrown up to a height h, the work done by gravity is W = mghW=Fd Simple and best practice solution for W=Fd equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itW= mgh In the figure below, a single frictionless rollercoaster car of mass m = 573 kg tops the first hill with speed v0 = 1




Prove Potential Energy P E Mgh With Figure Brainly In




Answered The Equation Used To Solve For Bartleby
Example 4 A 2 kg body free falls from rest from a height of 12 m Determine the work done by the force of gravity and the change in gravitational potential energy Consider the acceleration due to gravity to be 10 m/s 2 Solution Since, W = mgh Substituting the values in the above equation, we get W = 2 × 12 × 10 = 240 NSolution We need to solve for the moment that causes a 90 W = mgh = (8kg)(981 m/s2)(1m) = 785 Nm W = 785 Nm (b) The pin force is applied to point A, which does not move Therefore W = 0 (c) Using conservation of energy, we have T1 V1 = T2 V2 0 0 = 1 2 1 3 mL2 ω2 −mgh ⇒ ω = √ 6gh L = 6(981 m/s2)(1m) 2m ω = 384 rad/s 564 from the c 08 Pearson Education SouthQuestion Calculate The Work Done, W=mgh For A Mass Of 300 G Then, Using The Accepted Value For The Specific Heat Of Water, Calculate The Change In Heat, Q=cmw∆T For The Same Data Point Delta T Is 387 Degrees Celsius A) Calculate The Ratio W/Q B) Suppose Scale Used To Measure The Mass Of 300 G Was Not Properly Zeroed, And The Mass Was, In Fact 350 G Recalculate
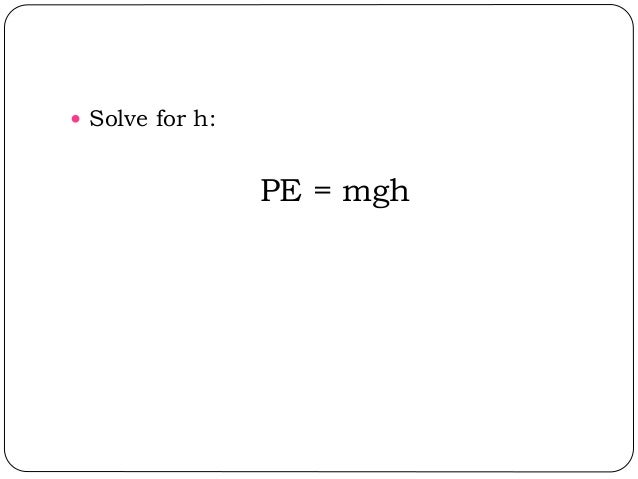



Inm Literal Equations Solving For One Variable
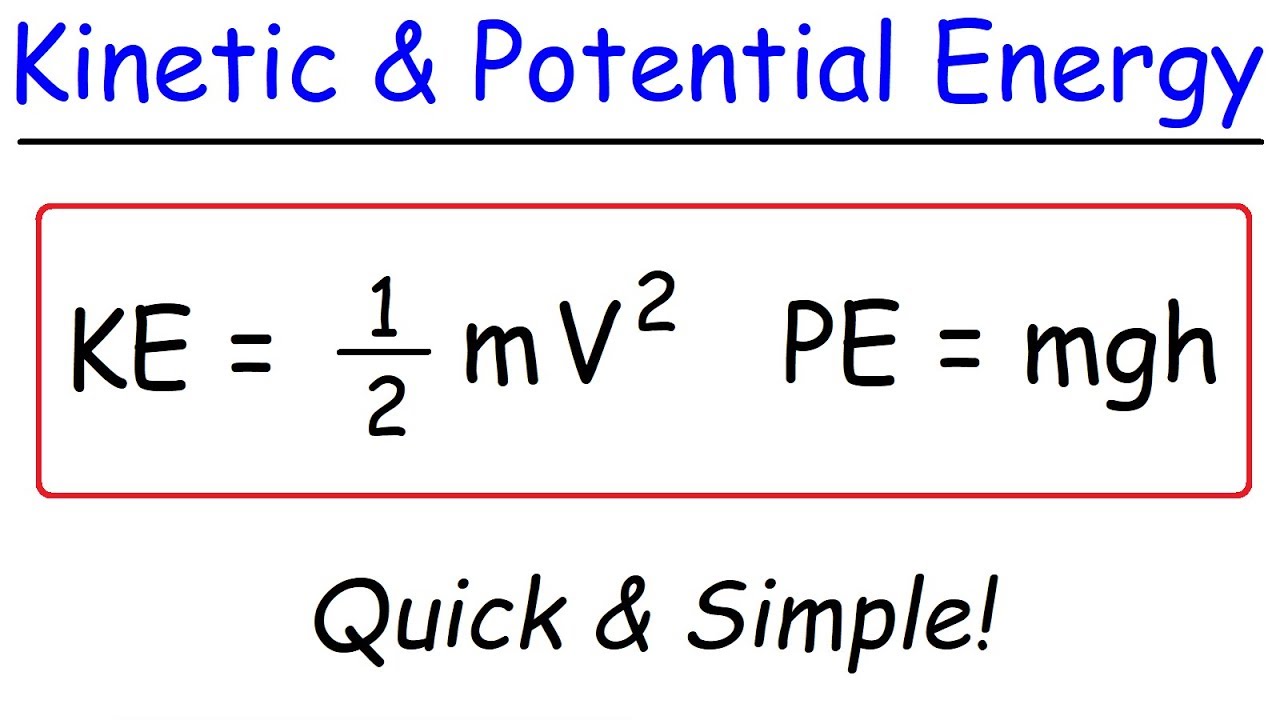



Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy Youtube
When the ball is at a height of 25 meters, the gravitational force has done an amount of work on the ball equal to W = mgh = 25 mg This work causes a change in velocity of the particle We now use the WorkEnergy Theorem, and solve for the final velocity · For example when a 10 kg book is lifted 05 m from the table, the force exerted in lifting the book is equal to its weight F=weight=mg The acceleration due to gravity, g is equal to 98 meters per second squared The work done in lifting the book is W=Fd where the displacement (d) is the height (h) to which the object is lifted W=mgh 51From the above equation W = mgh m = (sled) 80 (driver) 45 (equipment) *10 (dogs) m = 345 kg g = 981 m/s² (gravity constant)




Work And Energy I Work A Definition In




Solution
· according to COE, (initial)PE KE = PE KE (final) so i think that its better to use this instead of your equationFor example,if the object were to be released with some initial velocity,the KE (initial) would not be 0 so total initial energy is mgh1/2mv^2 instead of mghBtw,it is more precise to write change of PE = change of KE as this · define potential energy derive an expression for the gravitational potential energy of a body of mass m raised to a height h above the ground Physics TopperLearningcom 4q2uu7j77 Want to start a profitable Education Franchisee?Simple and best practice solution for W=mgh equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it Equation SOLVE Solution for W=mgh equation Simplifying W = mgh Solving




Solve V Mgh For M Multiple Choice Question Solving A Formula For A Variable Youtube




Openstax College Physics Solution Chapter 7 Problem 69 Problems Exercises Openstax College Physics Answers
Solve for force Solve for distance Solve for total work Where W = work W total = total work F = force d = distance m = mass v initial = initial velocity v final = final velocity References Books 1 ) Tipler, Paul A 1995 Physics For Scientists and Engineers Worth Publishers 3rd ed 2) Gittewitt, Paul 1993 Conceptual Physics Harper Collins College Publishers 7th ed Infant= 300 to the ground The coefficient of kinetic friction µ k = 02 At the bottom of the plane, the mass slides along a roughW= mgh ("h" is point B) In the figure below, a single frictionless rollercoaster car of mass m = 573 kg tops the first hill with speed v0 = 1 m/s at height h = 330 m C) How much work does the gravitational force do on the car from the initial point to point C?




Example Of The Two Column Ansv Style Solution Steps Are Animated And Download Scientific Diagram




Work And Energy Chapter 8 Mv 2 2 F 2 F3 Dr 4 P Dr F2 Dr F3 Dr 8 1 Kinetic Energy Pdf Free Download
P F v kN m s (6174 )(38 / ) A single force acts on a body that moves along an xaxis The figure below shows the velocity component versus time for the body For each of the intervals AB, BC, CD, and DE, give the sign (plus or minus) of the work done by the force, or state that the work is zero v A t BC D 2 0 2 0 2 1 W K K f K m v f v BC v C v B W 0 CD v D v C W 0 DE v E 0, v D 0 W 0Calculate the mass of the climber Solution Work = force × distance, so the work of lifting is w = m g h, where the force is F = m g and the distance is the height Rearranging to solve for mass gives w = m g h m = w g h m = 6250 J 98 m s 2 ⋅ 152 m = 6260 K g m 2 s 2 98 m s 2 ⋅ 152 mSolved The Problem Reads I Understand How W Mgh Force O Chegg Com For more information and source, see on this link https//wwwcheggcom/homeworkhelp/questionsandanswers/problemreadsunderstandwmghforcegravityxheightdeltak12mv2hencemgh1




Chapter 6 Work Amp Energy




Gravitational Potential Energy Problems And Solutions Basic Physics Basic Physics
· or, Total height of staircase = 45 * 15 / 100 = 675 m Work done would be equal to the Potential Energy possessed by the body ie W = mgh here, m = 50 kg , g = 10 m/s^2, h = 675 m Substituting the values, W = 50*10*675 And, Power = work done / time or, P = W / t or, P = 50*10*675 / 9 or, P = 375 W Therefore, The power is 375 W New questions in Physics WhatNow we can apply equation (11) to compute the work (force times distance) energy required Remember that the car has a mass m of 3000 kilograms (12) $ \displaystyle W = mgh = 3000 \times \times $ = 701 megajoules · Objective To have only one h and for it to be on its own on one side of = and everything else on the other side Change m and g into 1 so that h is on its own Divide both sides by mg giving P mg = mgh mg P mg = m m × g g × h But m m and g g both = 1 P mg = 1 × 1 ×h h = P mg Answer link




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf




Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator
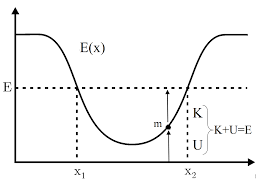
Always W = mgh as indicated in Example 7‐2 and Conceptual Checkpoint 7‐1 Solution 1 (a) The work done by gravity on the pine cone equals the increase in its kinetic energy Set the energies equal and solve for v 1 2 2 2 2 981 m/s 16 m 18 m/s2 WKmgh mv vgh 2The average molar mass of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the mole fractions of each gas (x i) multiplied by the molar mass (M i) of that particular gas latex\bar { M} =\sum _{ i }^{ }{ { x }_{ i }{ M }_{ i } }/latex Key Terms2 dp d jt F mK d mK jt dt d mK jt dt mK j t dt dt (11) Solving for K in (11), 1 2 42 2 1 2 K j t t m (12) 2 An object attached to a cord is moving in a circular path of radius 05m on a horizontal frictionless




3 Find Speed Ofend A When It Is At Point B A 25 1 H In 9 0 2gh In A 6 Van 1 2 A P3sh 1 4 14 Find Max Kinetic Energy Of Chain Before End




I Derive The Formula For Kin See How To Solve It At Qanda
· Plz solve this question on page Answers English, 1512 1750 Complete following passage by filling the gapsIndiaknown as a leader of entertainment Answers English, 1512 1750 Write a letter to your friend describing a place which you have visited recently Answers Math, 1512 1750 Anyone can joinGoogle meet Code=cxpwhhznjp AnswersM(g −v2/R Since n is always positive, its value is least when v is the greatest P2 In Fig 7, a single frictionless rollercoaster car of mass m = 5 kg tops the first hill with speed v 0 = 170 m/s at height h = 4 m How much work does the gravitational force do on the car/11/08 · Il a fallu des siècles aux savants pour faire la distinction entre le travail d'une force et la fatigue ressentie Le paradoxe c'est que la relation W = m g h laisse entendre que quand on marche à plat on ne devrait pas se fatiguer et qu'on devrait se reposer quand ça descend




Power Problems And Solutions




Solved Solve The Question Using The Laws Written On The Chegg Com
Solve for 1'2, the speed upon arriving at the trampoline E —E — 3mvl — i Inv, 1 = ± (45m/s)2 m) The speed is the absolute value of v (b) Now let subscript 3 represent the jumper at the maximum stretch of the trampoline, and x 7710ny/s, _½O, h o, represent the amount of stretch of the trampoline We have — — = 0, and xy — Y3 There is no elastic energy at position1 2 solve for p K p p mK 2m 2 Meanwhile, the statement that force is proportional to t means F is a constant multiple of t Call this constant multiple1 "j" 2 1 2 2 2 2 ;7 Replace each energy term with its formula and solve Notes For "the work done by gravity," use W = mgh For "the work done by the spring," use W = ½ k x2 If the question asks for the work done by any other force, use W = F d cosθ Work is positive if the force and the displacement are in the same direction (the force




Ppt Work Power Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Work
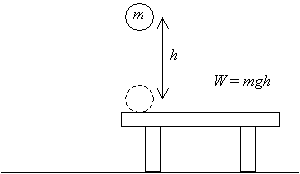
Gravitational potential energy is one type of potential energy and is equal to the product of the object's mass (m), the acceleration caused by gravity (g), and the object's height (h) as distance from the surface of the ground (the body) In this example, a 3 kilogram mass, at a height of 5 meters, while acted on by Earth's gravity would have 147 · W = Fs = 15 N × 4 m = 60 J Example 5 Calculate the work done in raising a bucket full of water and weighing 0 kg through a height of 5 m (Take g = 98 ms2) Solution Force of gravity mg = 0 × 98 = N h = 5 m Work done, W = mgh or W = 1960 × 5 = 9800 J• Therefore W = mgh • Grav potential energy = weight x height • Ep = mgh Section 42 Gravitational Potential Energy • The gravitational Potential Energy is equal to the work done and this is equal to the weight times the height • W = Ep = mgh • Example How much work is done lifting a 10 kg book to the height of 1m?



Solved Please Solve The All Parts Of The Questions And Sh Chegg Com




Solve This Stepwise 7 A Simple Pendulum Of Length 1 M Has A Bob Of Mass 10 G Physics Energy And Power Meritnation Com
Wait time TE after excitation before measuring M Shorter T2* spins have dephased z z z y y y vector sum x x x initially at t= TE MGHNMR Center Aside Magnetic field gradient Bo Gx x Bo Gx x Field from gradient coils Uniform magnet Total field z x G x wB z wx MGHNMR Center A gradient causes a spread of frequencies B o z z y MR frequency of the protons in a given location isThe procedure to use the potential energy calculator is as follows Step 1 Enter the mass, acceleration due to gravity, and height in the input field Step 2 Now click the button "Calculate Potential Energy" to get the Energy Step 3 Finally, the potential energy of the body will be displayed in the output field · Solve the following W = mgh = x (98) x 10 = 1960J The work done to take an object of mass kg to a height of 10 m is 1960 J Question 7 A body of 05 kg thrown upwards reaches a maximum height of 5 m Calculate the work done by the force of gravity during this vertical displacement Answer Given Mass (m) = 05 kg Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 98 m




Work And Energy An Introduction Work N




Ethiopia Learning Physics Grade 7 Page 276 In English
Mgh = 0500 kg 980 m/s 2 100 m = 490 kg ⋅ m 2 /s 2 = 490 J mgh = 0500 kg 980 m/s 2 100 m = 490 kg ⋅ m 2 /s 2 = 490 J 728 Note that the units of gravitational potential energy turn out to be joules, the same as for work and other forms of energyProblem A ball is dropped from a height of la m What is its velocity when it hits the ground?Use the ycomponent from part (c) and substitu




Potential And Kinetic Energy Problems Ppt Video Online Download




Let Us Consider An Equaiton 1 2 Mv 2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of The Body Upsilon Its Youtube
35 m h i d r d r rt r t Solve each equation for the variable specified 3 f epd, for e 4 12 g 31h 8g, for h 5 y mx b, for b 6 v r at, for r 7 3x c y 4, for c 8 5xy 2 n 6, for y 9 m n 2p 3, for m 10 6y z bc 2y, for y 11 3x 4y 7, for y 12 s (a t), for n 13 v r, for r 14 W mgh, for g 15 PV nRT, for V 16 G F D, for D 17 6t 62s (3tBecause Problem 15 ρ = pM RT the balance condition is pM = p M p which implies that M = ×M p This relation is valid in the limit of zero pressure (for a gas behaving perfectly) fINSTRUCTOR'S MANUAL 14 In experiment 1, p = Torr, p = Torr;Problem 4 Workkinetic energy object sliding on inclined plane and rough surface An object of mass m = 40 kg , starting from rest, slides down an inclined plane of length l = 30 m The plane is inclined by an angle of !



P3 Energy Work Power Mr Tremblay S Class Site
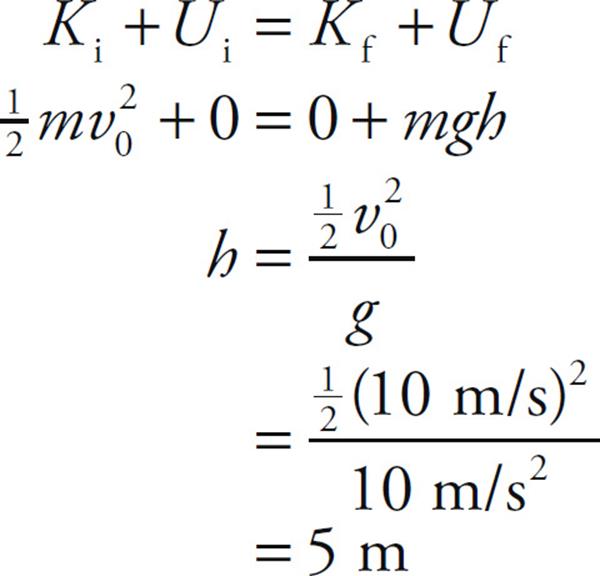



Work Energy And Power Content Review For The Ap Physics C Exam Ap Physics C Exam
Title Newton's Laws of Motion Author CBU Last modified by XP Created Date 6/15/1998 PM Document presentation format Onscreen Show (43)• Work = W = (10 kg) (98 m/s2) (1m) = 98 J • This isPotential energy of your marble at rest = m * g * h (m is mass in kg, g is earth's gravity =981 m/s^2 and h is the height above an arbitrary reference in meters could be the ground, sea level, whatever) As the marble changes height, it converts Potential Energy to Kinetic energy




Ch 6 Work And Enery




A W B E C W E D W E A Body Of Mass M Is
This shortcut makes it is easier to solve problems using energy (if possible) rather than explicitly using forces More precisely, we define the change in gravitational potential energy ΔPE g to be ΔPE g = mgh, where, for simplicity, we denote the change in height by h rather than the usual Δh Note that h is positive when the final height is greater than the initial height, and vice versa




Algebra Skills Proportional Reasoning Ppt Download




Potential Energy Formula And Sample Problem Pinoy Techno Guide




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics



Unit 4 Work And Energy Physics Project
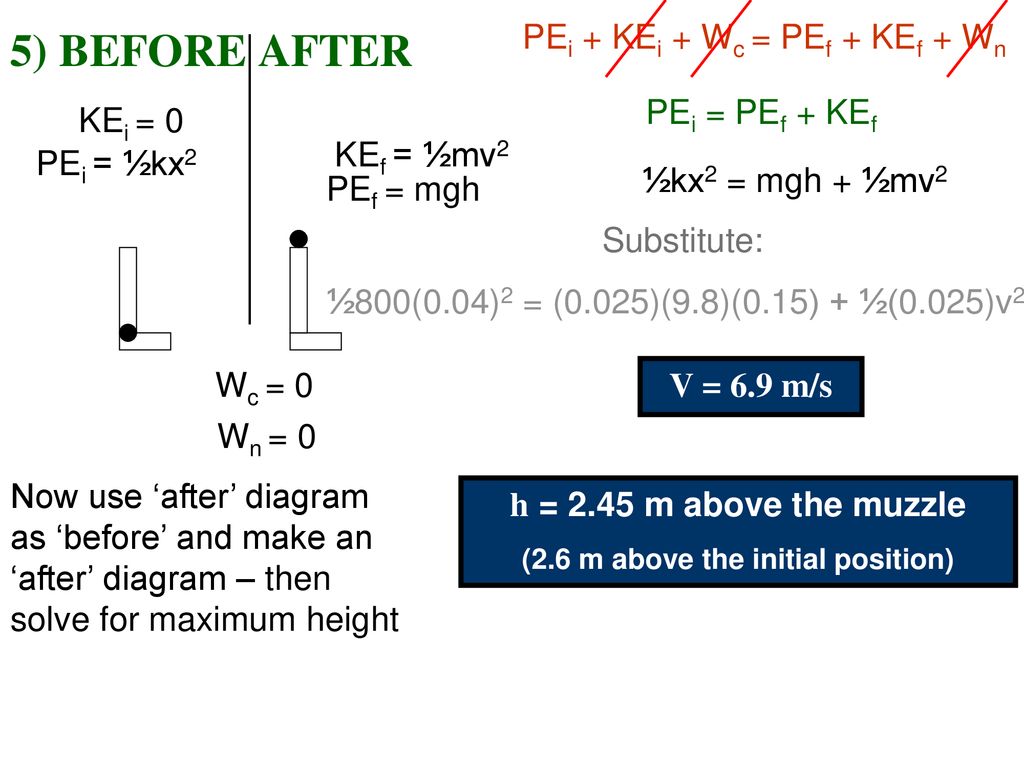



1 Before After 2 Before After Ppt Download




Understanding Work Energy Power Efficiency Energy Work Done




Understanding Work Energy Power Efficiency Energy Work Done




4 An Apple Has A Mass Of 0 2kg And Is Sitting On Gauthmath




Solved A Man Drops A 10 Kg Rock From The Top Of A 5 M Ladder W Self Study 365
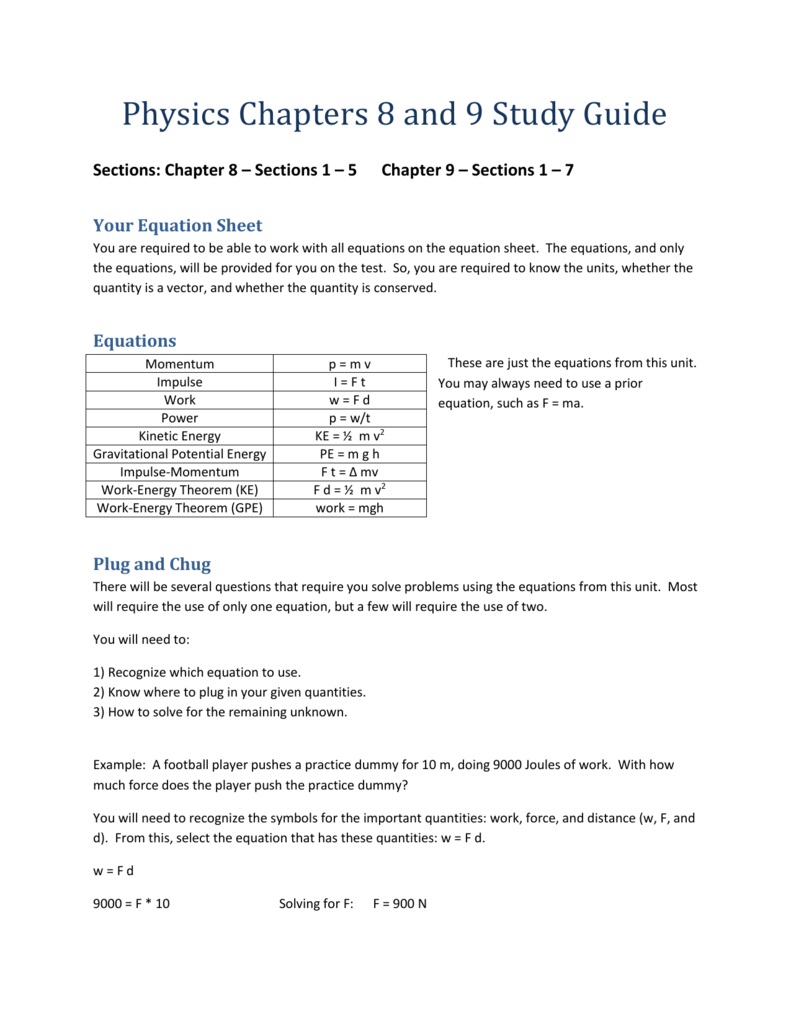



Your Equation Sheet




Mastering Physics Solutions Chapter 7 Work And Kinetic Energy A Plus Topper
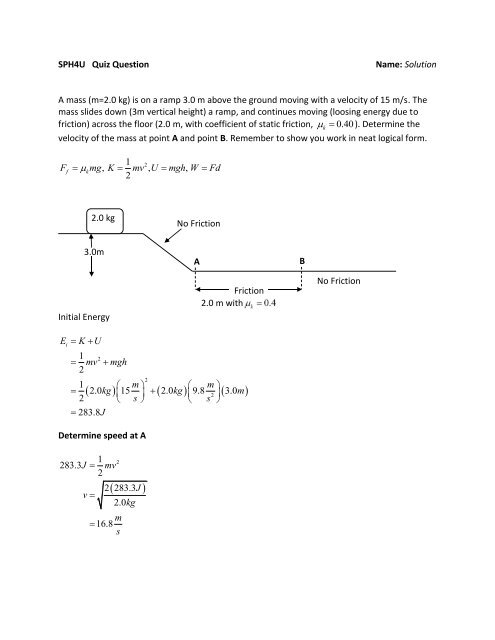



Sph4u Quiz Question Name Solution A Mass M 2 0 Kg Is On A




Error Using Mgh Intro To Physics Youtube



How To Calculate And Solve For Mass Height And Potential Energy The Calculator Encyclopedia Nickzom Blog




Consider A Drop Of Rain Water Having Mass 1 G Falling From A Height Of 1 Km It Hits The Ground With A Speed Of 50 M S Take G




Solved The Problem Reads I Understand How W Mgh Force O Chegg Com




Motion Revision Part 6 Of 8 Work Done By A Constant Force Energy Transformation Ppt Download




Kinetic And Potential Energy




Let Us Consider An Equation 1 2 M V2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of The Body V Its Velocity G Is The Acceleration Due To Gravity And H Is The Height Check




A Body Of Mass M Is Raised To Aheight H From The Surface Of The Ea



Chapter 6




Vertical Springs And Energy Conservation Video Khan Academy




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf




Comprehension 2 In Your Own Words Describe The Relationship Between A Bodys Course Hero




Htpibreview Ch6 P Mgh T Example Youtube
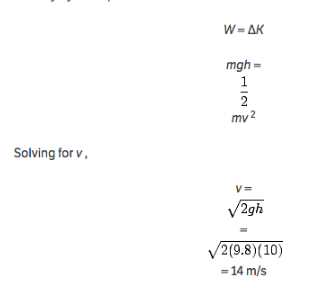



Get Answer A Ball Is Dropped From A Height Of La M What Is Its Velocity When Transtutors




Chapter 6 Work And Energy Pdf Free Download



What Is Kinetic Energy Universalclass




Unit 1 Module 2 Work And Energy




Learning Task 2 Problem Solving A Marble Is Thro Gauthmath




Work And Energy Work Can Only Be Done To A System By An External Force A Force From Something That Is Not A Part Of The System I Work A Definition Ppt




Energy 1 Energy The Word Energy In Todays




Physics Room Energy And Its Types For More Notes Like Facebook




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf




Understanding Work Energy Power Efficiency Energy Work Done




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics



New Page 1




Check The Correctness Of Equation 1 2mv2 Mgh Using Dimensional Analysis Method Brainly In




Ppt Chapter 10 Work And Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 662




Work Power And Energy Class 9 Extra Questions Science Chapter 11 Learn Cbse



Work Energy And Power Pdf Free Download




Openstax College Physics Solution Chapter 7 Problem 54 Problems Exercises Openstax College Physics Answers




How To Solve Physics Problems 7 Steps Instructables




Solved Use The Equations Below K 1 2mv 2 W F Delta X Chegg Com




The Total Mechanical Ene Descubre Como Resolverlo En Qanda




Chapter 4 Work Energy And Power
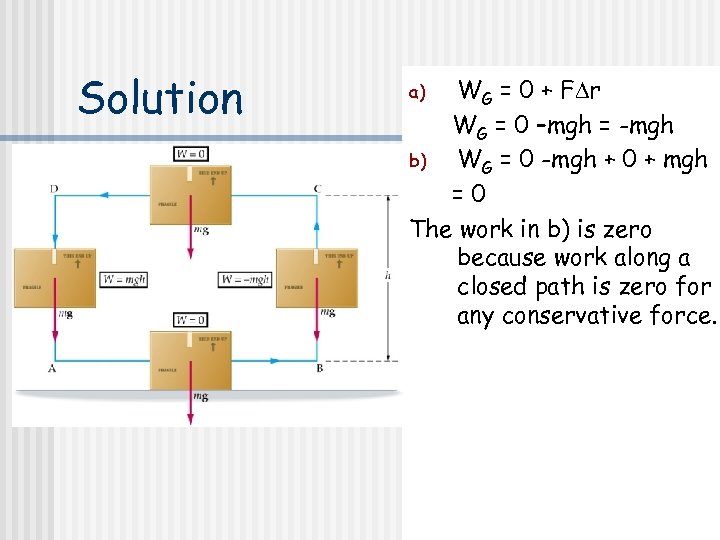



Work And Energy An Introduction Work N




Ppt Work Power Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Activity 11 15 An Object Of Mass Kg Is Dropped From A Height Of 4



Solved I Need Help To Solve These Qustions Course Hero



Solved In This Problem A Runner Must Overcome The Increas Chegg Com




Work And Energy An Introduction Work N




Show That The Sum Of Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy Is Always Conserves In The Case Of A Freely Falling Body Under Gravity With Air Resistance Neglected From A Height H By



Physics 1100 Work Energy Solutions




Physics Concepts And Problem Solving




Work And Energy I Work A Definition In




Kinetic And Potential Energy




Work Done Against Gravity




Htpib06c Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy Using Ep Mgh Youtube




Motion Revision Part 6 Of 8 Work Done By A Constant Force Energy Transformation Ppt Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿